ANSI/EIA 748 Compliance - EVM Software
Using Earned Value Management (EVM) systems (that comply with the ANSI/EIA 748 standard), organizations can combine and measure data on scheduling, resource allocation, costs and requirements to enforce efficient internal cost and scheduling protocols for projects, and to provide project managers and executives an effective system for tracking and forecasting project development and costs.
There are two objectives of Earned Value Management:
- To improve project and organizational efficiencies.
- To provide consistent, accurate information on project status.
EVPM compares the planned amount of work against what has actually been completed to determine if cost, schedule and work accomplished are progressing as planned. Work is "earned" or credited as it is completed.
This is accomplished by breaking down project work into budgeted and scheduled time-phased "planned value" segments, which combine to form the project baseline. Typically this is accomplished through establishing a Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) for the project. By establishing this structure, earned value analysis metrics such as Cost Variance and Project Schedule Indexes can be determined.
Successful incorporation of the Earned Value Project Management philosophy yields:
- Lowered costs through improved efficiencies.
- Earned value management provides an early warning system. It highlights projects that are off-track in time for corrective action to be taken.
- Increased productivity.
- Accelerated time to market.
- Improved accuracy in project time and budget tracking.
- Groundwork for effective decision-support systems.
Using Tracker Suite and Lotus Notes
Tracker Suite's Lotus Notes applications provide the organizational and tracking capabilities required for ANSI/EIA 748 earned value project management protocols:
- Project Tracker offers project templates for the WBS templates required for EVPM.
- Project status reports with automated reminders ensure that project activity and status are consistently updated.
- Web enabled timesheets, expense reports and purchase orders simplify reporting. Automatic approval routing structured in Personnel Tracker ensure legitimate approvals, and because these applications (Time Tracker, Expense Tracker and Purchase Tracker, respectively) integrate with Project Tracker, budgeting accuracy is improved for better reporting.
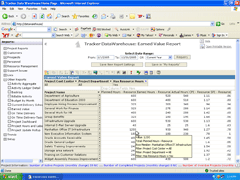
- The Tracker Data Warehouse generates over 42 report templates including budget vs. actual and on-time delivery schedules, reports based on the metrics required for earned value project analysis.
Looking for Web based solutions? TrackerSuite.Net, our 100% Web based version of Tracker Suite, also offers comprehensive features for Earned Value Management. Like Tracker Suite, TrackerSuite.Net also leverages Lotus Notes to simplify and streamline workflow. However, TrackerSuite.Net can also utilize other email platforms including Microsoft Outlook and Web based email services such as Gmail. A free demo is available, register today at www.TrackerSuite.Net/RFI for immediate access.
- Experience Tracker
- Register for a Demo Today
The 32 Criteria
The ANSI/EIA 748 standard defines 32 criteria for compliance. These ANSI/EIA 748 criteria can be broken into five main categories:
- Defining work and the organization.
- Planning and budgeting.
- Accounting.
- Analysis and reporting.
- Revision and maintaining data.
The criteria within each category are listed below.
- Defining Work and the Organization
- Define work elements within a Work Breakdown Structure (WBS).
- Define the organization and its business units.
- Integrate organizational processes, including planning, scheduling, budgeting, work authorization and cost accumulation processes.
- Identify organizational control or function for overhead (indirect) costs.
- Integration of WBS & organization structure information.
- Planning and Budgeting
- Schedule work sequentially, identifying task dependencies.
- Identify milestones and goals.
- Establish a time-phased budget for the planned work.
- Identify significant cost elements and establish budgets for them.
- Establish discrete work packages and their budgets.
- Determine that the sum of the work and planning budgets is within the control account budget.
- Identify level of effort activities.
- Determine overhead budget.
- Identify management reserves and undistributed budget.
- Reconcile program target cost goal with budgets and reserves.
Accounting
- Record direct costs.
- Summarize direct costs into the WBS.
- Summarize direct costs into the OBS.
- Record indirect costs.
- Identify unit, equivalent and/or lot costs.
- Accounting of material costs.
- Analysis and Reporting
- Generate monthly reports on cost and schedule variances.
- On a monthly basis, determine differences between planned and actual schedule and cost performances.
- Identify budgeted and actual indirect costs.
- Summarize data and variances.
- Implement management action dependent on variances.
- Update Estimate at Complete (EAC) costs.
- Revision / Data Maintenance
- Incorporate authorized changes.
- Reconcile current budgets to prior budgets.
- Control retroactive changes to records involving work performed.
- Prevent unauthorized revisions to budget.
- Document changes to Performance Measurement Baseline (PMB).